Have you ever looked up at the night sky and marvelled at the crisscrossing trails of aeroplanes? Have you ever wondered how air traffic controllers manage the movement of thousands of aircraft simultaneously, ensuring safety and efficiency in our busy airspace? The answer lies partly in a revolutionary technology called Aircraft 24 Radar. While “Aircraft 24 Radar” might not be the most precise term, it refers to using Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) technology to track aircraft in real-time. This article explores how ADS-B and its supporting infrastructure, like ground stations and platforms like Flightradar24, transform air traffic control and surveillance.
Demystifying ADS-B: A Smarter Way to Fly
Imagine a world where aeroplanes aren’t just passive participants in the air traffic system. ADS-B makes this a reality. Here’s how it works:
- Equipped to Talk: Modern aircraft are equipped with ADS-B transponders. These clever devices continuously broadcast data like the aircraft’s identification, position, altitude, speed, and heading.
- Seeing the Bigger Picture: A network of ground stations strategically placed around the globe receives these ADS-B signals. This network paints a real-time picture of air traffic, giving controllers a clearer view of what’s happening in their airspace.
- Beyond Line of Sight: Unlike traditional radar systems that rely on line-of-sight for detection, ADS-B works even over vast oceans and remote areas. This significantly improves controllers’ situational awareness, especially on long-haul flights.
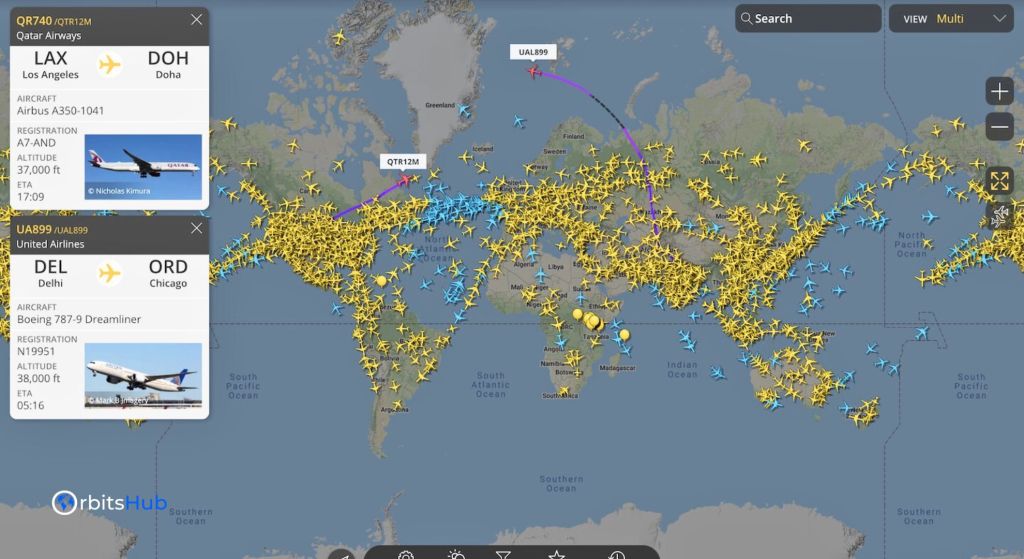
Benefits of Aircraft 24 Radar: A Multifaceted Approach
The widespread adoption of ADS-B and “Aircraft 24 Radar” systems brings a multitude of benefits to various stakeholders in the aviation industry:
- Enhanced Safety: With real-time information on aircraft position and trajectory, controllers can proactively manage potential conflicts and maintain safe separation between aeroplanes. As a result, fewer near-misses and collisions will occur while in the air.
- Improved Efficiency: Knowing exactly where each aircraft is allows for better route planning and optimization. This means shorter flight times, reduced fuel consumption, and lower airline operating costs.
- Streamlined Operations: ADS-B data can be integrated with air traffic management systems, enabling smoother traffic flow and reducing delays. This translates to a more pleasant flying experience for passengers.
- Transparency and Awareness: Platforms like Flightradar24, which utilize ADS-B data, provide real-time flight tracking information to the public. This empowers passengers to track their flights, check arrival times, and stay informed of delays.
The Road Ahead: Embracing the Future of Air Traffic Management
The impact of ADS-B and “Aircraft 24 Radar” is undeniable. It’s a significant step towards a more modern, efficient, safe air traffic management system. We can anticipate other innovations in the future as technology keeps on advancing:
- Satellite-based ADS-B: This will provide even more comprehensive coverage, particularly over remote areas where ground stations are scarce.
- Data Fusion: Integrating ADS-B data with other sources like weather information can further enhance controllers’ situational awareness and decision-making.
- Advanced Automation: Real-time data can automate some aspects of air traffic control, improving efficiency and reducing human error.

Addressing Challenges: Considerations for Widespread Adoption
While ADS-B offers a plethora of advantages, there are challenges to consider for its widespread adoption:
- Infrastructure Investment: Setting up and maintaining a dense network of ground stations can be expensive, especially for developing nations.
- Aircraft Equipage: Not all aircraft, particularly older models, are equipped with ADS-B transponders. Retrofitting entire fleets can be a significant cost for airlines.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: As with any data transmission system, ADS-B has potential cybersecurity risks. To protect sensitive information, stringent safeguards must be put in place.
Unveiling the Power of ADS-B: How It Works
ADS-B, or Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast, is a game-changer in aviation technology. It’s essentially a system that allows aircraft to broadcast their precise location, altitude, speed, and other vital information to air traffic control and other aircraft nearby.
- Transponder: Each aircraft equipped with ADS-B transponder continuously sends out this data.
- Ground Stations: A network of ground stations receives these transmissions, creating a real-time picture of air traffic.
- Data Sharing: The data is then shared with air traffic controllers, other aircraft, and third-party applications like Flightradar24.
By replacing traditional radar systems, ADS-B provides more accurate and detailed information, enhancing safety and efficiency in the skies.
A Safer Sky: How ADS-B is Enhancing Aviation Safety

ADS-B has significantly improved aviation safety by providing air traffic controllers with a more comprehensive and accurate view of the airspace.
- Collision Avoidance: By knowing the precise location of all aircraft, controllers can proactively identify and address potential conflicts, reducing the risk of collisions.
- Weather Avoidance: ADS-B data can be integrated with weather information to help pilots navigate storms and other hazardous conditions.
- Emergency Response: ADS-B data can quickly pinpoint the aircraft’s location in an emergency, facilitating a swift rescue operation.
To top it all off, pilots can now access data in real-time, which improves their decision-making and helps them keep a safe distance from other planes.
Beyond the Cockpit: Benefits of ADS-B for Passengers and Airlines
While ADS-B primarily benefits air traffic control and pilots, passengers and airlines reap significant advantages.
- Improved Flight Tracking: Passengers can monitor their flight’s progress in real time using apps that utilize ADS-B data.
- On-Time Performance: By optimizing flight paths and reducing delays, ADS-B contributes to improved on-time performance for airlines.
- Fuel Efficiency: Accurate flight planning based on ADS-B data can help airlines save fuel by optimizing routes and altitudes.
- Environmental Impact: Reduced fuel consumption leads to lower carbon emissions, making aviation more environmentally friendly.
Overall, ADS-B enhances the overall passenger experience and airline operations.
Challenges and Opportunities: The Future of ADS-B
Key Aspects of ADS-B and Aircraft 24 Radar Systems
Explanation of Segments
- Enhanced Safety (25%): Includes measures for collision avoidance, weather avoidance, and emergency response capabilities.
- Improved Efficiency (20%): Focuses on better route planning, reduced fuel consumption, and lower operating costs for airlines.
- Transparency and Awareness (15%): Highlights the public’s ability to access real-time flight information, enhancing transparency.
- Infrastructure Investment and Equipage (15%): Addresses the financial and logistical challenges of setting up ADS-B systems and upgrading older aircraft.
- Cybersecurity Concerns (10%): Emphasizes the importance of safeguarding the data transmitted by ADS-B systems from potential cyber threats.
- Future Developments (15%): Discusses upcoming advancements like satellite-based ADS-B, data fusion, and increased automation in air traffic management.
Despite its numerous benefits, the widespread adoption of ADS-B is challenging.
- Infrastructure Costs: Building and maintaining a robust ground station network requires significant investment.
- Aircraft Equipment: Older aircraft may need to be retrofitted with ADS-B transponders.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting the sensitive data transmitted by ADS-B is crucial.
However, these challenges are being addressed, and the future of ADS-B is promising.
- Satellite-Based ADS-B: Expanding coverage to remote areas.
- Data Analytics: To improve efficiency and safety, utilizing ADS-B data for advanced analytics.
- Integration with Other Systems: Combining ADS-B with other technologies for a more comprehensive air traffic management system.
The importance of ADS-B in determining the trajectory of aviation’s future will only grow as technology advances.
Revolutionizing Air Traffic Control: The Role of Aircraft 24 Radar
Aircraft 24 Radar, a term often used interchangeably with ADS-B, is transforming the way air traffic control operates.
- Real-Time Situational Awareness: Controllers have a constant, accurate picture of the airspace.
- Increased Capacity: By optimizing airspace usage, ADS-B enables more flights to operate safely.
- Reduced Workload: Automation powered by ADS-B can streamline specific tasks for controllers.
- Improved Decision Making: Access to real-time data enhances controllers’ ability to make informed decisions.
The combination of ADS-B and advanced air traffic management systems lays the foundation for a more efficient and secure aviation industry.
A Collaborative Approach for a Safer Sky
The success of Aircraft 24 Radar relies on a collaborative effort between governments, aviation authorities, airlines, and technology providers. Continued investment in infrastructure, technological advancements, and standardized regulations will be crucial to unlocking this revolutionary system’s full potential.
Are you considering implementing ADS-B solutions or navigating the ever-evolving world of air traffic management? You can work with OrbitsHub, an industry-leading maritime and aviation consulting service provider. With extensive experience, our team of professionals is well-versed in ADS-B technology and its uses. We can help you explore solutions tailored to your needs and ensure you stay ahead of the curve in this dynamic industry. Get in touch with OrbitsHub today, and let’s discuss how we can help you navigate the exciting future of air traffic control!
Related FAQs
How does Flightradar24 track aircraft?
Satellites equipped with ADS-B receivers collect data from aircraft outside our terrestrial ADS-B network’s coverage area and send that data to the Flightradar24 network. Satellite-based ADS-B data available on Flightradar24 comes from multiple providers.



