The HMS Beagle was launched in 1820, primarily as a survey vessel designed to map out the coastline of South America. It wasn’t meant to be a ship of discovery; it was simply another naval vessel performing routine duties for the British Admiralty. However, it was far from ordinary in the adventures it would later embark upon. Under the command of Captain Robert FitzRoy, the Beagle set sail on its first voyage in 1826, and this voyage would eventually become the ship’s most significant contribution to science.
FitzRoy, a highly skilled and ambitious naval officer, was tasked with surveying the coast of South America, but he also sought to make a name for himself as a scientist. This was where Darwin entered the picture. In 1831, Charles Darwin, then a young, aspiring naturalist, was invited to join the HMS Beagle on its second voyage, which was set to take it around the world.
The Voyage: A World-Changing Expedition
The voyage that began in 1831 was not just any regular expedition. The Beagle’s route took it across the Atlantic Ocean, around the southern tip of South America, and through the Pacific, visiting places such as the Galápagos Islands, Australia, and several regions of South America. Along the way, Darwin made keen observations, collected specimens, and kept detailed notes on the plants, animals, and fossils he encountered. These observations became the foundation for his revolutionary theories.
One of the most significant aspects of the Beagle’s journey was its stop at the Galápagos Islands in 1835. It was here that Darwin made the observations that would eventually lead to the formulation of his theory of natural selection. The differences he noted between the finches on the islands became a cornerstone of his later work. The birds’ varying beak shapes demonstrated how species could adapt to their environment, a revolutionary concept at the time.
The Beagle’s voyage was not only an important scientific journey for Darwin but also one that helped shape the scientific community’s understanding of the world. Darwin’s work on this voyage was instrumental in laying the foundation for modern evolutionary biology, geology, and ecology.
The Impact of the Voyage: A New Way of Thinking
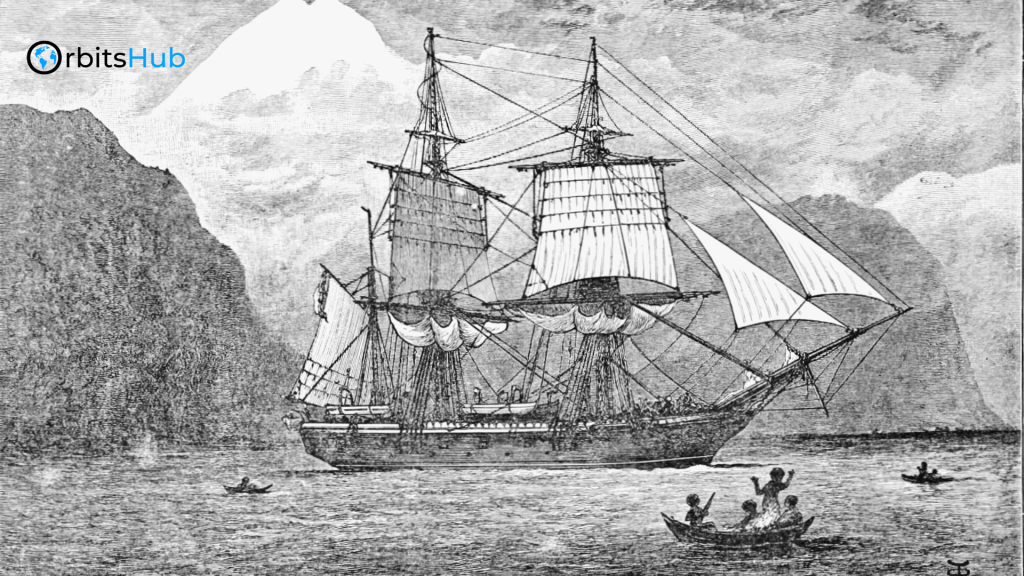
The HMS Beagle’s journey and Darwin’s observations profoundly changed the scientific world. Darwin’s notes and specimens became the basis of his book On the Origin of Species, published in 1859. This work would go on to change the way humans understood the origin and development of life on Earth. The concept of natural selection, as detailed in the book, challenged traditional views and sparked fierce debates among scientists, religious leaders, and philosophers.
Darwin’s idea of evolution by natural selection was groundbreaking because it gave scientists a way to explain the variety of life on Earth. Many people thought that species were created by God and had not changed since they were first made before this idea came along. Darwin, through his work on the Beagle and his subsequent studies, showed that species could evolve over time based on environmental pressures, creating a dynamic and ever-changing world of life forms.
The voyage also had a profound effect on geology. Darwin’s studies of the formations in South America, particularly in the Andes Mountains, helped to establish the idea of gradual geological processes shaping the Earth over millions of years. This was in direct contrast to the prevailing theory of catastrophism, which suggested that the Earth’s features had been shaped by sudden, violent events.
The Beagle’s voyage not only helped cement Darwin’s place in history but also changed the way the world looked at the natural world and its history. It led to the development of many new branches of science, such as ecology and evolutionary biology. It also had a significant impact on fields like anthropology, genetics, and palaeontology.
The Legacy of the HMS Beagle
The legacy of HMS Beagle lives on today. It continues not only through the impact of Darwin’s work but also through the ship’s symbolic importance in the history of science. The ship’s journey reinforced the belief that science could answer questions about the natural world. It also emphasised the significance of exploration and observation in scientific discoveries.
Today, the HMS Beagle’s journey is seen as a model for scientific exploration. Modern scientific expeditions continue to build on the principles established by Darwin and the Beagle’s crew. The legacy of the Beagle also highlights the importance of interdisciplinary work in scientific discovery. Darwin was not just a naturalist; he was also a geologist. Additionally, he researched animal behaviour and contributed to multiple fields of study.
The Fascinating End of the Beagle’s Journey

After returning from its famous second voyage, the HMS Beagle continued to serve as a survey vessel for several more years. However, by 1870, after serving its purpose, the ship was decommissioned. The Beagle was eventually sold for scrap and broken up in 1872. Despite its unremarkable end, the Beagle’s impact on science and the world was far-reaching.
Darwin completed his research during the voyage. He then went on to write his groundbreaking book, The Voyage of the Beagle, which is a firsthand account of the journey. This book remains a vital work for understanding the scientific context of the 19th century. The Beagle played a pivotal role in shaping modern science.
Key Stats from the Beagle’s Journey
- The HMS Beagle’s second voyage lasted almost five years, from 1831 to 1836.
- Darwin collected over 1,500 specimens of plants, animals, and fossils during the voyage.
- The ship visited many countries, including Brazil, Argentina, Chile, the Galápagos Islands, Australia, and South Africa.
- The Beagle’s journey covered a distance of approximately 40,000 miles.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is the HMS Beagle so important in the history of science?
A very important part of Darwin’s work on the idea of evolution by natural selection was the HMS Beagle. Its journey transformed our understanding of biology, geology, and ecology. It marked a turning point in how scientists perceive the world.
2. What impact did the HMS Beagle have on the scientific community?
The Beagle’s voyage played a crucial role in establishing evolution as a scientific theory. It also introduced the concept of natural selection and significantly influenced various fields of science, including geology and anthropology.




