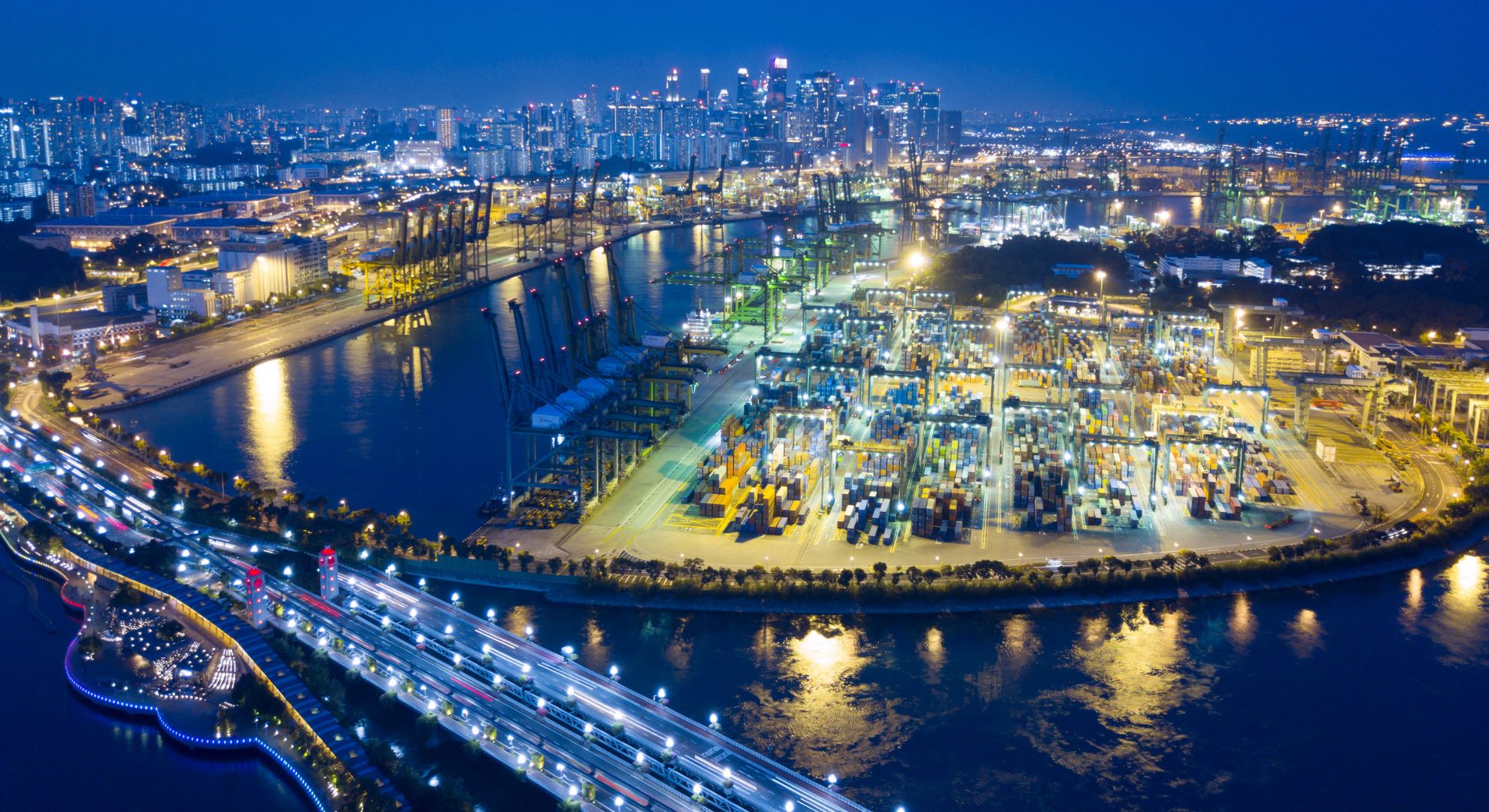
An important player in international trade, the Port of Singapore is a thriving maritime center at the intersection of key shipping lanes. With an illustrious history spanning centuries, this port has grown from a modest trading post to a colossal entity, contributing significantly to Singapore’s economic prosperity.

A Historical Perspective
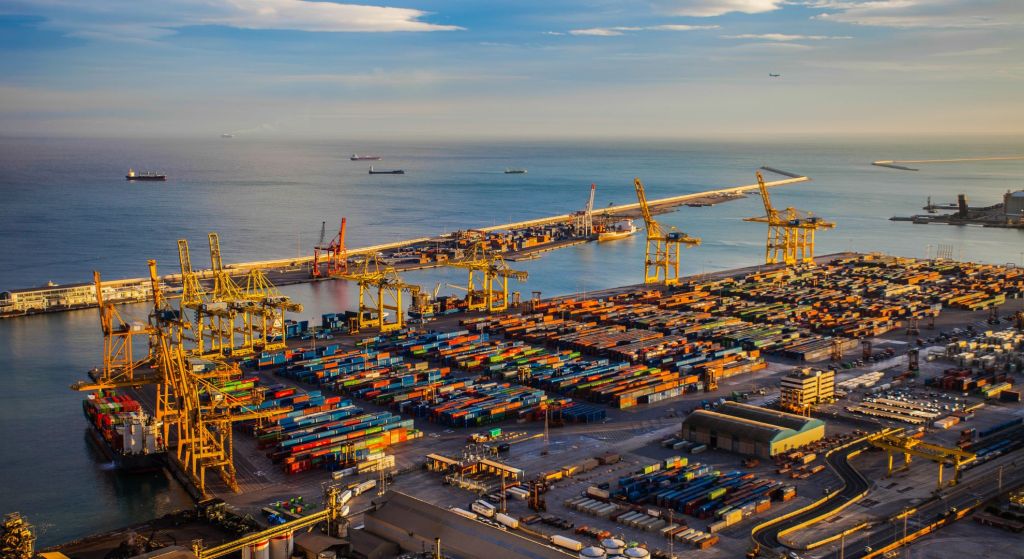

Ancient Beginnings
The Port of Singapore’s maritime legacy dates back centuries. As early as the 13th century, the island served as a trading post for merchants from different parts of the world. However, it was during the British colonial era in the 19th century that the port began its transformation into a maritime center of strategic importance. Recognizing Singapore’s potential, Sir Stamford Raffles, a British colonial official, established a trading post on the island.
Colonial Era and Growth
Raffles, noting the potential of Singapore’s natural deep-water harbor, established a trading post for the British Empire on the island. Ships transporting textiles, spices, tea, and opium would make frequent stops at the port due to its advantageous position at the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, which enabled it to take advantage of the expanding trade between Europe and Asia.
Post-Colonial Developments
Following the end of British colonial rule, the Singaporean port continued to thrive. The port grew and expanded throughout the fast industrialization of the 1960s and 1970s, making it an important economic driver for Singapore. A major turning point in the port’s history came in 1964 with the founding of the Port of Singapore Authority (PSA).
State-of-the-Art Infrastructure

The Port of Singapore stands as a testament to modern maritime engineering and innovation. With a vast network of terminals and berths, the port has the capacity to handle millions of containers, bulk cargo, and liquid commodities annually.
Advanced Terminals
The Port of Singapore boasts an array of advanced terminals, including those at Tanjong Pagar, Keppel, Brani, Pasir Panjang, Sembawang, and Jurong. These terminals, equipped with state-of-the-art automated cranes and equipment, facilitate the swift loading and unloading of containers, reducing turnaround times and optimizing operational efficiency.
Digitalization and Innovation
The Port of Singapore is a pioneer in port digitization, utilizing data analytics and the Internet of Things (IoT) to streamline logistics and supply chain management. The Smart Port initiative has transformed the Port of Singapore into a model of efficiency, minimizing delays and bottlenecks while ensuring maximum utilization of resources.
Economic Impact
As a global maritime hub, the Port of Singapore plays an indispensable role in international trade, connecting continents and facilitating the flow of goods across the world. The port’s efficiency and reliability have made it the preferred choice for industries such as manufacturing, electronics, and oil and gas.
Contribution to GDP
The Port of Singapore contributes significantly to the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and provides thousands of jobs in various sectors, including shipping, logistics, and maritime services.
Role in Global Trade
The port’s strategic location along major shipping routes has turned Singapore into a vital transshipment hub, where cargo from various origins is consolidated, transshipped, and redistributed to destinations worldwide.
Sustainability Initiatives
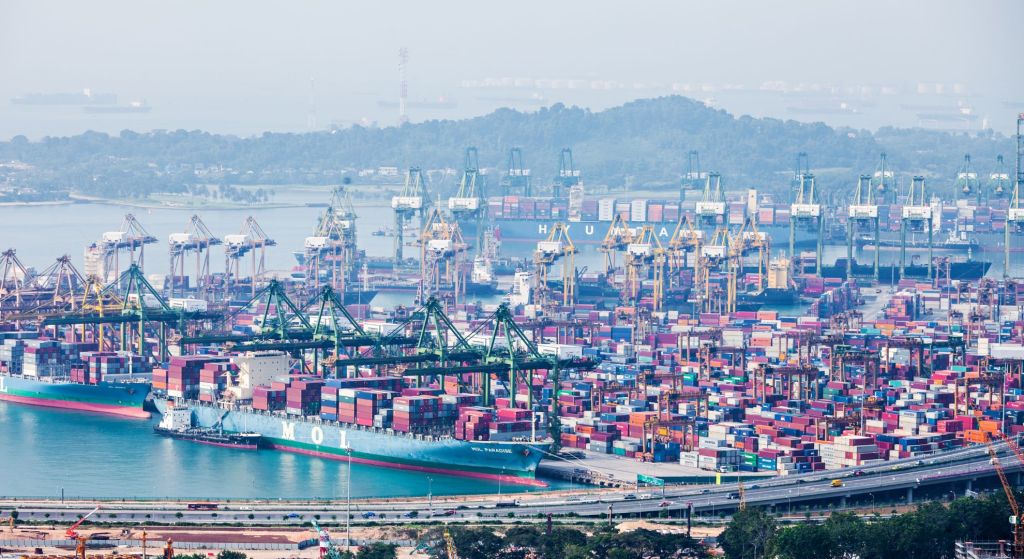

The Port of Singapore has taken proactive steps to become a leader in sustainability within the maritime industry. One of the port’s notable sustainability initiatives is the implementation of shore-to-ship power technology, also known as cold ironing.
Environmental Stewardship
The Port of Singapore actively collaborates with industry stakeholders, academia, and government bodies to foster innovation and drive sustainable practices. It supports research and development projects focused on green technologies, alternative fuels, and eco-friendly vessel designs.
Future Outlook
Despite its remarkable achievements, the Port of Singapore faces various challenges in an ever-evolving maritime landscape. To stay ahead, the port must remain agile and adaptive, leveraging its reputation for efficiency and innovation to attract new business and retain existing customers.
Upcoming Developments
Long-term infrastructure development plans, such as the Tuas Mega Port project, will further enhance the port’s capabilities, solidifying its position as a global maritime giant. The port can stay ahead of the competition in the digital age by adopting new technology like autonomous vessels, blockchain, and artificial intelligence.
Related FAQs
What is the historical significance of the Port of Singapore?
The Port of Singapore has a rich maritime legacy dating back to the 13th century. It evolved from a trading post into a strategic maritime center during the 19th-century British colonial era, contributing significantly to Singapore’s economic prosperity.
How did the Port of Singapore contribute to post-colonial economic growth?
Following the end of British colonial rule, the port thrived and played a pivotal role in Singapore’s industrialization during the 1960s and 1970s. The founding of the Port of Singapore Authority (PSA) in 1964 marked a major turning point, solidifying its importance.
What makes the infrastructure of the Port of Singapore state-of-the-art?
The port boasts advanced terminals equipped with automated cranes and modern equipment at locations like Tanjong Pagar, Keppel, Brani, Pasir Panjang, Sembawang, and Jurong. This infrastructure enables the swift loading and unloading of millions of containers annually.
How does the Port of Singapore contribute to sustainability in the maritime industry?
The port has implemented shore-to-ship power technology, or cold ironing, as part of its sustainability initiatives. It actively collaborates with stakeholders for green technologies, alternative fuels, and eco-friendly vessel designs, promoting environmental stewardship.
What are the upcoming developments for the Port of Singapore?
Long-term infrastructure plans, including the Tuas Mega Port project, aim to enhance the port’s capabilities. To stay ahead in the digital age, the port is exploring new technologies such as autonomous vessels, blockchain, and artificial intelligence for continued innovation.