Tidal levels and chart datums play a crucial role in maritime navigation, coastal engineering, and various other applications. Understanding the concept of the Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) is essential for estimating water depths and ensuring safe navigation.
What is the Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT)?

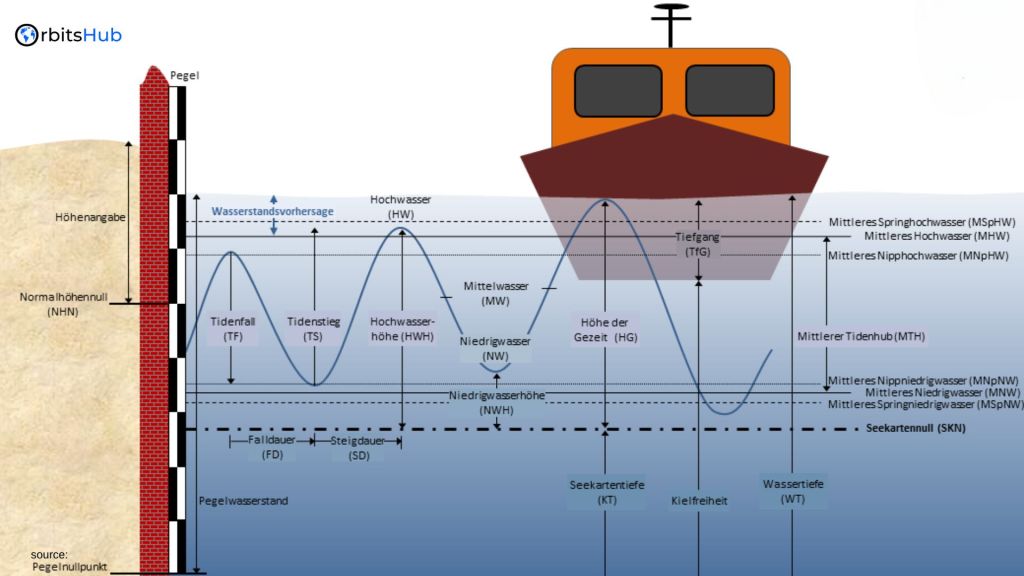
The Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) is a standard chart datum used in nautical charts to determine water depths. It represents the lowest possible level based on lunar and solar gravity. Since water levels below LAT can occur due to weather influences, such as high air pressure or a seaward breeze, it is crucial to understand the concept of LAT and its implications for maritime activities.
Relationship between LAT and Other Chart Datums
While LAT is the standard chart datum for nautical charts, other vertical datums are used in different applications. Mean Sea Level (MSL), for example, is used in the offshore industry and oceanography. The separation between MSL and LAT varies depending on the location. Additionally, estuaries often use a level called Approximately LAT (ALAT) due to the influence of river water on water levels. It is important to note that each nautical chart specifies the datum used to avoid confusion.
Factors Affecting Tidal Levels
Tidal levels are influenced by various factors, including lunar and solar gravitational forces, weather conditions, air pressure, wind direction, and river discharges. High air pressure can cause a drop in tide levels, while strong winds blowing directly along a narrow channel can also affect water levels. It is essential to consider these factors when estimating water depths and planning maritime activities.
Determining LAT and Other Chart Datums
The determination of LAT and other chart datums involves a combination of scientific calculations, data analysis, and reference points. The North Sea Hydrographic Commission (NSHC) coordinates the determination of chart datums for the North Sea region. However, each country may have different LAT levels at its maritime boundaries. The geoid, a hypothetical global shape of the ocean’s surface unaffected by wind and tides, is also used to define LAT in relation to the so-called ellipsoid.
Practical Implications of LAT
Understanding LAT has practical implications in various industries and applications. In maritime navigation, knowledge of LAT helps mariners determine safe water depths and avoid grounding. It is crucial for port authorities, lockkeepers, and vessel operators to have accurate information on water levels, especially in areas with significant tidal variations. LAT is also important in coastal engineering projects, offshore operations, and environmental monitoring.
Navigating with LAT Information
For mariners, accurate and up-to-date information on LAT is essential for safe navigation. Nautical charts provide details on water depths and reference levels, including LAT. By combining the charted depth with the tidal height, mariners can determine the true depth of water. If there are updates or changes to the LAT values in any particular area, be sure to check the relevant charts and stay updated.
Different Vertical Datums: LAT, MSL, and NAP
In addition to LAT, other vertical datums are used in different contexts. Mean Sea Level (MSL) is commonly used in offshore operations and oceanography. It represents the average water level over a long period of time. Another important reference level is the Amsterdam Ordnance Datum (NAP), which is the national reference level for height on land in the Netherlands. NAP reflects the mean water level for Amsterdam in the absence of water motion.
Height Measurement Using GPS Receivers

One method to determine height is to utilize a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver. To determine height, the level of MSL or the geoid is first established in relation to the GPS receiver’s internal reference, known as the ellipsoid. The LAT values are then subtracted to calculate the height above LAT. This method allows for precise height measurements in relation to the chosen vertical datum.
Importance of Accurate Chart Datum Information
Accurate chart datum information is crucial for safe and efficient maritime operations. Mariners, coastal engineers, and other professionals rely on precise data to make informed decisions and mitigate risks. It is essential for hydrographic offices, port authorities, and relevant organizations to provide up-to-date and accurate chart datum information to ensure the safety and success of maritime activities.
The Role of LAT in Coastal Management
The Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) is crucial in coastal management as a fundamental reference point for various activities and decisions. Here’s how LAT is integral to coastal management:
- Baseline for Coastal Development: LAT is often used as a baseline for planning and developing coastal infrastructure, such as sea defenses, harbors, and waterfront properties. It helps engineers and planners determine safe elevations to protect against tidal flooding.
- Environmental Monitoring: LAT assists in assessing the health of coastal ecosystems. Providing a standard reference level enables consistent monitoring of tidal ranges and sediment deposition, which are vital for understanding coastal erosion and habitat changes.
- Navigational Safety: LAT data is essential for ensuring the safety of vessels navigating near coastal areas. Accurate LAT measurements help design navigation aids, such as buoys and markers, which indicate safe passage routes during low tide conditions.
LAT and Its Impact on Marine Construction Projects
Marine construction projects, such as building docks, marinas, and offshore platforms, require precise knowledge of tidal levels to ensure safety and functionality. The Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) is particularly significant in this context:
- Foundation Design: LAT is used as a benchmark for designing the foundations of marine structures. It ensures the structures are built above the lowest possible tide levels, preventing submersion and structural damage during low tide conditions.
- Dock and Slip Design: LAT helps design docks and slips to accommodate varying water levels. It ensures that boats and ships can safely moor at low tide without grounding, critical for maintaining operational efficiency.
- Erosion Control Measures: LAT data is crucial for implementing erosion control measures. By understanding the lowest water levels, engineers can design practical barriers and revetments to protect against coastal erosion and stabilize shorelines.
Comparing LAT with Other Tidal Datum Systems
Understanding different tidal datum systems is essential for accurate navigation, construction, and coastal management. The Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) is one such system, but there are others, each with unique applications:
- LAT vs. Mean Sea Level (MSL): LAT represents the lowest tide levels predicted based on astronomical factors, while MSL is the average sea level over a long period. Mean Sea Level (MSL) is commonly used in offshore engineering and oceanography, providing a baseline for measuring sea level rise and climate change impacts. In contrast, LAT is more relevant for navigation and coastal construction, providing a conservative estimate of the lowest tide levels.
- LAT vs. Mean Lower Low Water (MLLW): MLLW is another tidal datum representing the lower average of the two daily low tides. It is commonly used in the United States for nautical charting. LAT is lower than Mean Lower Low Water (MLLW) and provides a more conservative estimate for the lowest possible tide, making it useful for planning and safety in regions with significant tidal fluctuations.
- LAT vs. Mean High Water (MHW): MHW is the average of all high tides observed over a specific period. It serves as a reference for defining coastal boundaries and property lines. Unlike LAT, which focuses on the lowest tide levels, MHW helps understand the highest tide levels and their potential impacts on coastal infrastructure and development.
- LAT vs. Amsterdam Ordnance Datum (NAP): In the Netherlands, NAP is used as a reference level for all height measurements, including water levels. It reflects the mean water level in Amsterdam without tidal influences. On the other hand, LAT accounts explicitly for the lowest tide levels, making it a critical reference for navigation and marine construction in tidal waters.
Advanced Technologies for Measuring LAT
The accurate determination of the Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) relies on advanced technologies and methodologies. If you want precise and trustworthy data, you need these technologies:
- Satellite Altimetry: This technology uses satellites equipped with altimeters to measure sea surface heights. It provides large-scale data coverage and helps determine LAT by capturing long-term sea level trends and variations. Satellite altimetry is particularly useful for remote or inaccessible areas.
- Tide Gauges: Tide gauges are installed at various coastal locations to measure water levels continuously. These gauges record tidal data, which is then analyzed to determine LAT. They are crucial for capturing local tidal patterns and variations, providing high-resolution data for navigation and coastal management.
- Global Positioning System (GPS): GPS technology assists in determining precise locations and elevations. By integrating GPS data with tidal observations, accurate LAT values can be established. This method is beneficial in areas with complex topography or where traditional tide gauge data may be lacking.
- Data Integration and Analysis: Integrating various data sources, including satellite, gauge, GPS system, and LiDAR data, enhances the accuracy of LAT measurements. Experts use data fusion and machine learning to hone these observations even more to get a complete picture of how tides work.
Case Studies: Navigating Challenges with LAT Data
Understanding and effectively using the Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) data can present various challenges. Here are some case studies illustrating how these challenges have been addressed:
- Port of Rotterdam, Netherlands: For safe navigation and port operations, the Port of Rotterdam—one of the world’s biggest and busiest ports—depends on precise LAT data. Problems develop because sedimentation and tide patterns are constantly changing. The port uses a combination of tide gauges, satellite data, and hydrodynamic models to maintain accurate LAT measurements. Regular dredging is conducted based on LAT data to ensure safe depths for incoming and outgoing vessels.
- Great Barrier Reef, Australia: The Great Barrier Reef’s varied water depths and intricate coral structures make it a challenging navigational target. LAT data is critical for ensuring that vessels avoid damaging the reef. The Australian Maritime Safety Authority (AMSA) utilizes advanced GPS and hydrographic survey techniques to update nautical charts with accurate LAT data. This effort helps protect the reef ecosystem while ensuring safe passage for vessels.
- Thames Estuary, United Kingdom: The Thames Estuary is characterized by significant tidal variations and complex water movements. LAT data is essential for flood risk management, navigation, and environmental protection. Using hydrodynamic models and tide gauges, the Environment Agency and the Port of London Authority (PLA) work together to monitor the water level. LAT data helps plan flood defenses and maintain navigational channels.
Understanding the concept of the Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) is vital for safe and efficient maritime navigation. LAT serves as a standard chart datum, representing the lowest possible water level based on lunar and solar gravity. Weather and river flows are two of the many variables that can affect tide levels, so keeping them in mind is crucial. Different vertical datums, including Mean Sea Level (MSL) and Amsterdam Ordnance Datum (NAP), are used in various applications. Accurate chart datum information and height measurements are essential for mariners, coastal engineers, and other professionals involved in maritime activities. Our maritime initiatives can be safely and successfully executed if we stay informed and use accurate data.
Related FAQs
What is the lowest astronomical tide and mean lower low water called?
A chart datum is generally derived from some tidal phase, in which case it is also known as a tidal datum. Common chart datums are lowest astronomical tide (LAT) and mean lower low water (MLLW).




